The Fourth Industrial Revolution and Industry 4.0 are often used interchangeably but, ” the Fourth Industrial Revolution is Digital Transformation itself. However, digital transformation is not limited to industry. We are witnessing Digital Transformations in finance, medicine, education, and media as well.
That said, Industry 4.0 can be used in all Industrial contexts where processes need to be more intelligent.It’s a digital transformation in the industrial sector towards a new stage in the organization and control of the industrial value chain. The industrial value chain can refer to tasks a company performs to produce a valuable product.
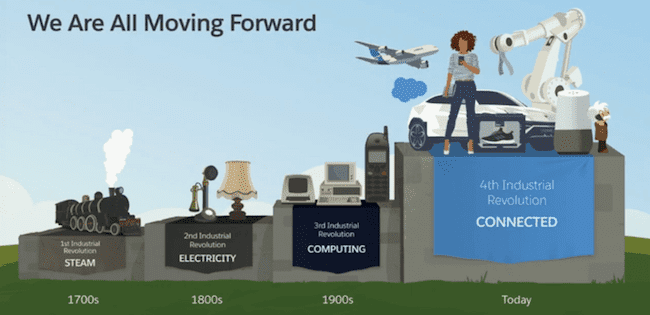
What about the other 3 Industrial Revolutions?
The first industrial revolution ran from the end of the 18th century to the beginning of the 19th century and during this time, steam was invented.
The next or second I.R. started at the end of the 19th century, with massive technological advances including electricity.
The third revolution started during the second half of the 20th century and featured nuclear energy and electronics, including telecommunications and computers.
Presently, cyber physical systems or intelligent computers are shaping the Fourth Industrial Revolution discussed below
https://www.salesforce.com/in/blog/2020/04/what-is-the-fourth-industrial-revolution-4IR.html
What are cyber-physical systems?
A cyber-physical system (CPS) is the new generation of intelligent, digital systems composed of physical hardware capabilities and computing software techniques. Optimizing functionality, autonomy, reliability and safety, CPS is a major step for future technology that could change and improve lives for the better.
“Examples of CPS include smart grid, autonomous automobile systems, medical monitoring, industrial control systems, robotics systems, and automatic pilot avionics
Precursors of cyber-physical systems can be found in areas as diverse as;
- aerospace, automotive, chemical processes,
- civil infrastructure, energy, healthcare, manufacturing,
- transportation, entertainment, and consumer appliances.”
Cyber-physical systems form the basis of Industry 4.0 (smart machines).
In essence, Industry 4.0 is the trend towards automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies and processes which include;
- cyber-physical systems (CPS),
- the internet of things (IoT),
- industrial internet of things (IIOT),
- cloud computing,
- cognitive computing
- artificial intelligence.
Automation is a term for technology applications where human input is minimized. This includes business process automation (BPA), IT automation, personal applications such as home automation and more.
*Automation can use AI (artificial intelligence); however, the majority of automation utilizes traditional software to move data from one place to another. The difference between AI and automation is that AI aims to simulate human thinking. Put another way; automation works with data — AI ‘understands’ data.’
Data exchange helps deepen the knowledge of markets and customers by providing insights.
“With the data available to them in data exchanges, organizations can enrich their statistical and machine learning models, enhance analyses and forecasts, create more in-depth profiles of their customers, and much more.
I will provide brief definitions regarding important elements of Industry 4.0 and if it sparks your curiosity, you can dig deeper!
Other technologies involved in Industry 4.0
Analytics
A field of computer science that uses math, statistics, and machine learning to find meaningful patterns in data. Analytics – or data analytics – involves sifting through massive data sets to discover, interpret, and share new insights and knowledge.
What is the relationship between Artificial Intelligence and quantum computing?
“This makes quantum computing the perfect candidate for powering artificial intelligence.The vast amounts of data processed by AI systems require enormous computational power. Quantum computers have the potential to provide that power and thus enable AI to reach its full potential.”
3D Printing
‘The Fourth Industrial Revolution is said to have extensive dependency on 3D printing technology. Some advantages of 3D printing for industry are;
- that 3D printing can print many geometric structures, as well as simplify the product design process.
- It is also relatively environmentally friendly.
- In low-volume production, it can also decrease lead times and total production costs.
- Moreover, it can increase flexibility, reduce warehousing costs and help the company towards the adoption of a mass customization business strategy.’
3D printing is transforming many industries, including the medical, construction and space . With 3D printers now having the ability to create human skin, sustainable housing and space craft!
Machine learning (ML)
This is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that ‘learn’, that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so.
Lastly, this catchy title.
The Internet of Things (IoT) describes the network of physical objects—“things”—that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the internet. These devices range from ordinary household objects to sophisticated industrial tools. With more than 7 billion connected IoT devices today, experts are expecting this number to grow to 10 billion by 2020 and 22 billion by 2025
There are a few other technologies involved like cloud and cognitive computing, 5G and more not included in this post., so as not to bog you down.
Potential casualties from Industry 4.0
Is there a downside to this unfolding digital transformation?
According to the 2018 report by the World Economic Forum; “These transformations, if managed wisely, could lead to a new age of good work, good jobs and improved quality of life for all, but if managed poorly, pose the risk of widening skills gaps, greater inequality and broader polarization.”
The Fourth Industrial Revolution’s technologies, such as artificial intelligence, genome editing, augmented reality, robotics, and 3-D printing, are rapidly changing the way humans create, exchange, and distribute value. As occurred in the previous revolutions, this will profoundly transform institutions, industries, and individuals.
Additional side effects and or concerns.
- With Big Data and hyper-connectivity there are increased concerns about privacy and or cybersecurity risk.
- and ethical concerns around the usage of private data
- Will the providers of intellectual and physical capital; shareholders receive the biggest cut?
Job loss
Artificial intelligence and automation are expected to have the most significant impact on employment figures within the global workforce.
The 4th Industrial Revolution ( Industry 4.0) will impact nearly every industry with The Economist predicting that 50% of jobs are vulnerable to automation.
In recent decades, as automation has emerged as the central competitive factor in manufacturing operations across the globe, the use of industrial robots has grown substantially. In 1970 the total number of industrial robots in use in the US was 200. By 1980, that number had risen to 4,000, and by 2015, it was 1.6 million. There are estimated to be more than 3 million industrial robots in use today.
It is predicted that new jobs and other opportunities would also be created during this digital transformation.
Brian

